Fistula on gum
A fistula on the gum or fistula is quite common in dentistry, especially when it comes to pediatric practice. Contrary to the popular opinion of patients, a fistula is not a separate nosological form (disease), it is just a symptom.
Fistula on the gum: features in children and adults
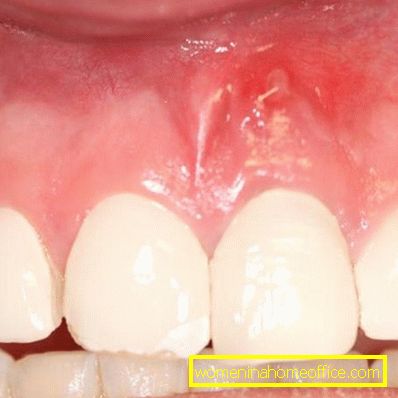
Fistula is defined as a hole for outflow of exudate (pus). Studying education under the microscope shows that it is lined with mucous membrane, therefore, the hole can not be closed until there is an irritating factor, namely the separation of pus.
The main reason for the formation of a fistula is purulent processes in the area of the tooth root, in other words, periodontitis is inflammation of the surrounding tooth tissue, often with purulent manifestations. Trivial caries can provoke periodontitis, which has been left untreated for a long time and turned into complicated forms - pulpitis, and then periodontitis.
There are some features of fistula in childhood and adult practice. So the physiological situation is that in children all diseases of the maxillofacial area occur much faster and quite often, caries and even pulpitis go unnoticed, and the child comes to a dentist’s appointment with a fistula.
A fistula on the gum in a child often scares parents, and for good reason. The danger lies in the possible damage to the primordia of the permanent teeth, in the case of milk bite. In addition, the presence of a purulent process in the oral cavity is a permanent source of infection for the children's body.
The formation of a fistula is often accompanied by an increase in body temperature, a deterioration in the general condition of the body, an increase in regional lymph nodes and the inability to fully feed. There is no need to talk about the presence of pain!
In adult practice, fistula formation will be more noticeable. Often, patients complain of pain during biting, the presence of an unpleasant smell from the mouth. And the causative tooth itself can be sealed or be under the crown, in rare cases an extensive carious cavity can be observed. Rarely, among the reasons that are characteristic only for adult practice is the dentist's mistake during treatment, the establishment of intracanal pins, when perforation of the tooth root occurs, followed by inflammation.
Symptoms of fistula formation, as well as in children, are similar. First of all, it is a aching, throbbing pain, which is aggravated by biting, an increase in body temperature, the presence of a through hole in the area of the apex of the root with purulent discharge.
An abscess on the gum: how to treat?
Fistula treatment can only be carried out in a dental chair with preliminary research. The main goal of treatment is the destruction of the source of pus and infection, the elimination of all factors that will contribute to its formation.
In pediatric practice, the treatment of fistulas is associated with some physiological features, namely, age-related features of tooth development, milk or permanent bite. Often, but only under strict indications, such teeth are removed. Otherwise, the child undergoes long-term treatment of the canals of the teeth - cleaning them, followed by disinfection, treatment of root inflammation, only after this - setting the seal. Sometimes intracanal treatment can not be carried out, since the roots of milk teeth can be absorbed, in which case the tooth is immediately removed. Permanent teeth, after their eruption, also have no formed roots, in the case of periodontitis, they are removed. Therefore, parents should strictly follow, to prevent the development of even pulpitis in the baby with a constant bite.
Fistula treatment in adult practice follows the same principle, there are practically no physiological features. But there may be other complications, namely the presence of orthopedic structures, fillings, sealed root canals (wrong, which caused the formation of periodontitis).
It is worth remembering that the treatment of fistulas can not take place in one session - this is a long process not only in the dentist’s chair, with the mechanical treatment of root canals and the laying of anti-inflammatory drugs, it is also antibiotic therapy. If conservative methods of treatment do not give any results, then the tooth should be removed.
The treatment of fistula at home deserves special attention - it is not possible! No medicinal herbs, no matter how anti-inflammatory effect they have, cannot cope with localized purulent infection, especially dental. This is a job for antibiotics!

Under a categorical ban, all warm compresses, which easily and quickly provoke complications - the involvement of the tops of the roots of neighboring teeth into the purulent process, the formation of cysts, abscesses and phlegmon.
The only acceptable use of traditional medicine can be called a complex treatment in tandem with the methods of traditional medicine.
Fistula treatment can be carried out exclusively in the dentist’s chair, using modern methods, in combination with local and general treatment. After the canals are cleaned, a period of pus removal begins, as the main source of infection is antibiotics, rinsing the mouth with special solutions, after which the medicine is placed in the root canal and the temporary filling is closed. Only after a certain period of time, without recurrence of the disease, can the causative tooth be sealed. The patient remains in the dispensary at the dentist.